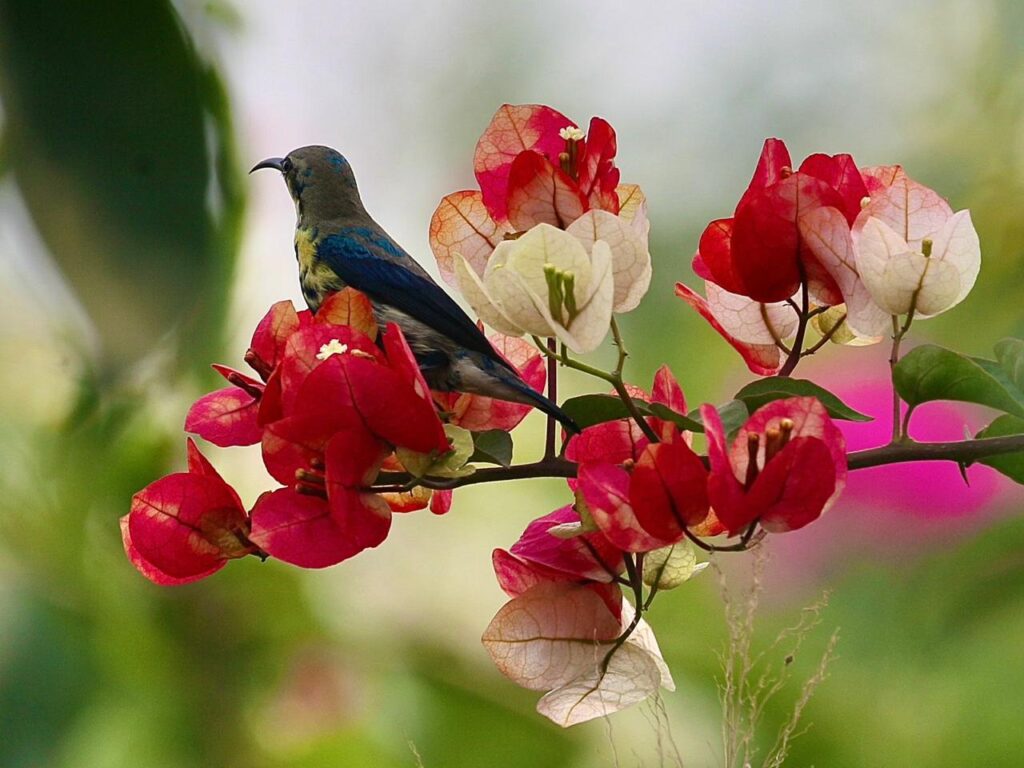

Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including the diversity and range of species, genes, and ecosystems, whereas local biodiversity refers to the variety of life within a particular local area. Local biodiversity in particular plays a very vital role, as it provides essential ecosystem services and supports the well-being of local communities. With the emphasis on local biodiversity, our focus on ‘Native flowers for local biodiversity’ became crucial in today’s time as many people started to grow non-native plant flowers in their gardens for aesthetic and commercial purposes without having proper information about their ill effects on the local environment. This ultimately resulted in the extinction of native flowers, which in turn affects the ecological balance and our planet loses its ability to provide many of the things we all need to survive.
Benefits of Native Flowers:
Planting native flowers can provide us with various benefits. Native plants offer a feast for the senses with their stunning show of colorful flowers, abundant fruits and seeds, and captivating seasonal transformations that paint landscapes in vibrant hues from the tender greens of spring to the fiery reds and yellows of autumn. Yet, their beauty goes beyond aesthetics. By opting for native plants in your landscaping, we are not just creating visually stunning surroundings; we are also fostering healthier environments for ourselves and for our community as a whole. Unlike traditional lawns that rely on heavy doses of synthetic chemicals, native plant landscapes provide natural havens that require fewer artificial fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides, reducing chemical pollution and promoting healthier ecosystems. Moreover, landscaping with native plants offers a host of additional benefits, from combating climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide to conserving precious water resources, making it a sustainable choice for both the environment and your wallet.
Simply put, the choice of plants we add to our gardens and landscapes can have an impact on biodiversity, with native plants providing the greatest benefit. Our native plant life supports native insect populations, which in turn support larger animals, creating a “food web” of interconnected species.
Local Conservation Efforts:
Community-based conservation efforts at the local level for native flowers are grassroots efforts aimed at preserving and promoting the biodiversity of native floral species within a community. By engaging residents, schools, businesses, and local organizations, communities can undertake various initiatives to protect native flowers and their habitats. These efforts may include organizing community gardening projects, establishing native plant nurseries, hosting educational workshops, and advocating for policies that support native flower conservation.
Restoring degraded habitats at the local level for native flowers is a crucial endeavor that embodies community-driven conservation efforts. By recognizing the importance of preserving native flora and the habitats they depend on, communities can take proactive steps to revitalize damaged ecosystems. Through initiatives such as removing invasive species, replenishing soil nutrients, and replanting native flowers, local residents can actively participate in the restoration process.
Native Flowers Selection Process:
Maximizing biodiversity benefits begins with identifying native plant species adapted to our landscape’s unique conditions. These are some ways to select native flowers: consulting reputable sources for species native to the region and habitat; mimicking natural layers by incorporating wildflowers, grasses, shrubs, and trees; encouraging natural intermingling; and including habitat features like brush piles and nesting boxes. Moreover,skillfully integrating native plants with non-invasive ornamentals and planning for continuous bloom to support pollinators are important processes for selecting native flowers.
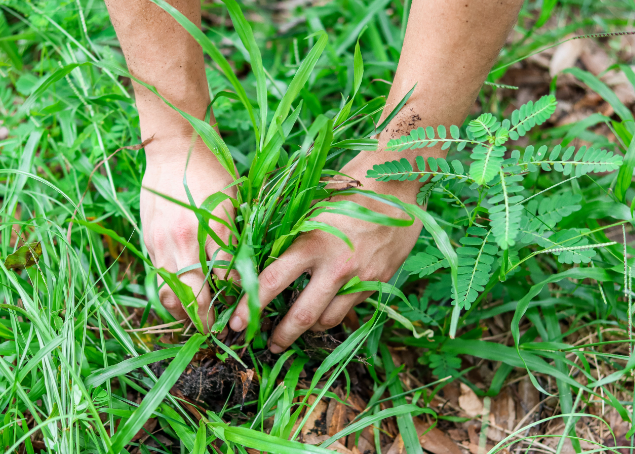

Conclusion:
Native plant gardening serves as a vital link between backyards and biodiversity conservation, offering a powerful opportunity to repair fragmented ecosystems and bolster struggling pollinator networks. By selecting native species for our gardens, we not only enhance the beauty of our surroundings but also provide essential resources such as food and shelter for birds, insects, and other vulnerable wildlife. With passion and persistence, gardeners can collaboratively transform even the smallest of yards and green spaces into interconnected landscapes that nurture both human and environmental well-being.
About the author: Ranjana Vishnoi
Ranjana is from Jodhpur, Rajasthan. She is currently pursuing a BA Honours in Political Science from Hindu College, University of Delhi and is very passionate about the environment.
